

Heat Detection Methods
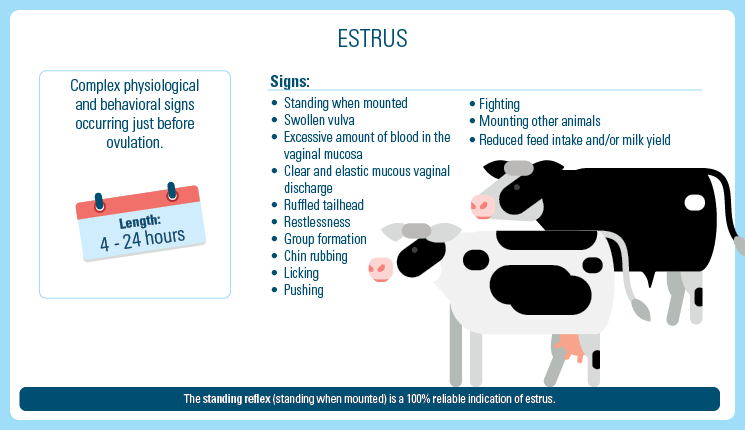
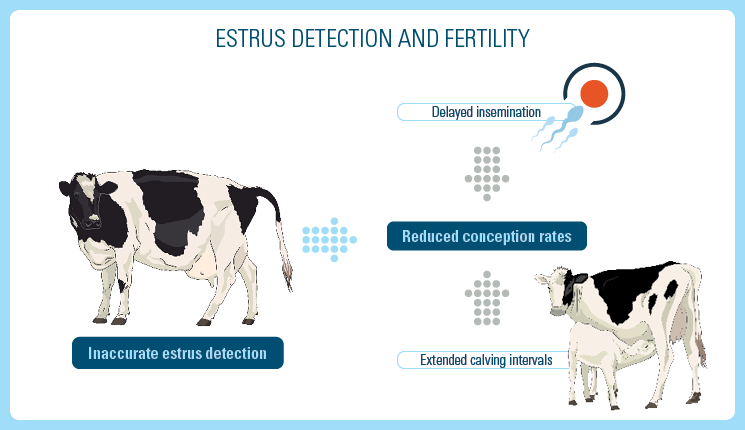
Estrus detection is a very critical component of first service insemination efficiency. Identifying the cows that do not conceive is equally critical.
Being able to interpret cow behavior and other signs requires looking two to three times a day for around 20 minutes, along with good record keeping and training for those doing heat detection.
Heat Mount Detectors
The simplest method is tail paint. This method requires a strip of brightly colored paint to be applied to the midline area in front of the tail head. When the cow is mounted during standing heat, the paint is rubbed off by mounting cows. Each individual cow needs to be observed every day. Paint sticks or crayons are other alternatives which work on the same principle as tail paint.
Scratch Cards
Scratch cards can either come with a self-adhesive back or may require the use of glue to apply them to the base of the cow’s tail. When mounting activity occurs,the scratch card is rubbed and changes color to indicate that the cow may need to be served.
Teaser Animals
Teaser animals (vasectomised bulls) will mount a cow in heat. It still requires someone to observe the standing heat. They may be equipped with a chin ball marker to mark cows that they are mounting so that actual observation of standing heat is not required.
Disadvantages:
- Aggressive behavior
- Favoritism (ignoring non favorite cows in heat)
- Vectors of venereal diseases (vasectomised bulls)
Pedometers
Pedometers are sensors that are placed on the front leg of the animal. They are a highly-efficient and accurate method of estrous detection.
When a cow is in heat, there is a large spike in activity relative to when it is not in estrous. By measuring the number of steps using pedometers, a cow in estrous can be identified.
Disadvantages:
- Cow-to-cow variation
- Comparisons only for an individual cow against her baseline level of activity
- High initial investment in the technology
TV Surveillance
This method involves camera surveillance and the recording of the behavior of cows in a confined area.
Disadvantages:
- Requires careful evaluation of a day’s recordings
- Subjective interpretation of the cow’s behavior
Automated Heat Detection
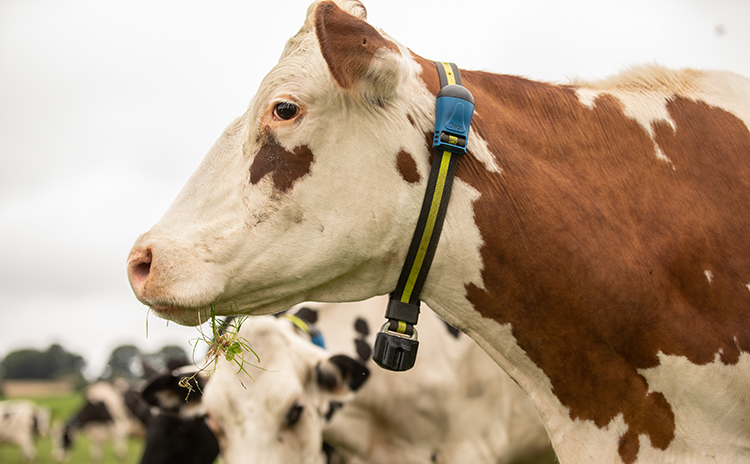

Different Automatic Heat Detection technologies have been available for the past years to detect cows in heat. The technology has evolved from simple sensors attached to one of the cow’s legs (pedometers) to more sophisticated collar or eartags sensors that combine movement activity and ruminantion parameters. Allflex Livestock Intelligence reproduction monitoring applications enable beef and dairy farmers to optimise conception rates, while reducing labour and time. Leveraging behavior monitoring based on activity, rumination, eating and other proprietary key cow behaviours, Allflex applications provide unmatched heat detection accuracy, delivering actionable insight in real time, with precise insemination timing guidance.

